Using multi-factor authentication increases the security for logging in to websites significantly. But what happens when your phone is lost and you lose access to all your multi-factor keys?
1. Explanation
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) means that when logging in to a website or application you have to provide multiple ways of proving your identity before you can log in. This can be 2 methods or more. This can be a password and an SMS passcode or email passcode and SMS passcode, or other combinations. These days due to the many breaches many user passwords are out on the internet. Many companies are using a form of MFA to protect their infrastructure and it is also recommended that individual people use MFA to protect themselves.
Usually, when a person uses MFA, this MFA will consist of 2 methods to prove the identity. Usually, a password and a passcode are derived from your phone through SMS/authenticator APP or e-mail. I prefer the authenticator APP method, I will explain more about this below.
You might have already thought, this is all good and sounds secure but what if I lose access to 1 or more of the methods required to login to a website or application. I will go over multiple ways to recover access.
2. Password Manager
A password manager is a tool that helps you to remember, create and store your passwords so you only need to remember one master password and you never have to type passwords anymore.
2.1 Why password manager?
Passwords are everywhere, almost every site and application requires you to have an account. It is almost impossible for a person to use a different password for all these sites and applications and remember which password was used for each. A password manager will help you to generate a unique password and auto-fill this password for future logins. Thanks to the password manager you only need to remember one password and that is the master password of your vault. This vault is the place of the password manager that will store all your passwords.
Of course, you could use the same password in every website and application but that is strongly discouraged. Because you do not know how and where those websites and applications store your passwords. If only one of these companies gets breached and your password is leaked on the internet then you will need to change your password on all the other sites. Remember, when using the same password everywhere, your password is only as strong as the security of the least secure company where you used this same password.
My mail address is part of 6 separate breaches but thanks to using a password manager it was easy to change my password for only these 6 websites.
2.2 Different password managers
There are many password managers available these days. I would suggest using a password manager from a respected vendor. I have used LastPass before and shifted to Bitwarden and never looked back. I would recommend to use Bitwarden to anyone who asks me.
3. Multi-factor authentication methods
There are many multi-factor authentication methods and these can all be used in combination with each other depending on what the website or application supports. To get an idea of which places support multi-factor authentication you can check on https://2fa.directory/.
4 factors can be part of multi-factor authentication:
- Something in your possession: security token, bank card, a key, time-based one-time passcode, …
- Something you know: password, pin, passphrase, …
- Something you are: fingerprint, face, eyes, …
- Somewhere you are: GPS coordinates of your current location, …
We will be concentrating on the authenticator app which provides time-based one-time passcodes.
3.1 Time-based one-time passcodes
Time-based one-time passcode (TOTP) are passcodes that are generated by an authenticator application which is usually installed on your phone but can also be built into a hardware security token.
The place where you want to log in will generate a long secret key. This key will usually be transferred to the authenticator by scanning a QR code. With this secret key and the Unix timestamp (independent of timezones), the authenticator can generate a TOTP while using an algorithm.
When you need to log in, both your authenticator and the website will create a TOTP passcode so when you fill in your passcode the website will compare both passcodes to verify if they are the same.
3.2 SMS or e-mail
SMS and e-mail are used a lot for providing a passcode to the user for login. This method is better than no MFA but both are having security or ease of use issues.
There are multiple ways a hacker can get a hold of the SMS messages, they can be intercepted by swapping out the SIM card or ordering a copy of the SIM card.
E-mail is slow to get the passcode and the e-mail account can be hacked.
3.3 Hardware security token
A hardware security token is secure but it is overkill for most users and has a certain difficulty to start due to requiring to buy this hardware device.
4. Authenticators
There are many authenticators and each of them provides a different user interface and other backup methods.
Researched authenticators backup method:
- DUO: backup to Google Drive with an encryption key
- Google Authenticator: create a QR code and scan QR code for recovery
- Microsoft Authenticator: backup to OneDrive
- Authy: backup in the cloud with a password
I choose DUO because it provides the best backup and restore method for my use case and because it is part of Cisco which is a respected company. I don’t feel confident I can securely store the QR code for Google Authenticator, Microsoft not requiring a password for accessing the keys, and having to trust Twilio Authy for cloud storage are all reasons why I chose DUO.
5. Usage of Bitwarden and DUO
Bitwarden is the password manager and DUO is the authenticator I use.
5.1 Bitwarden Phone and DUO Phone
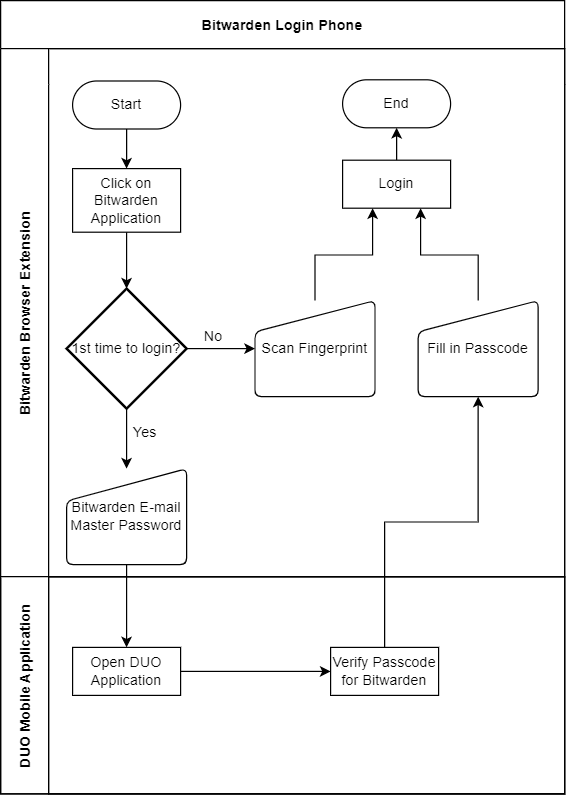
Below you can find a flowchart to show how I usually log in to any website or application when using the Bitwarden application on my phone.
5.2 Bitwarden PC and DUO Phone
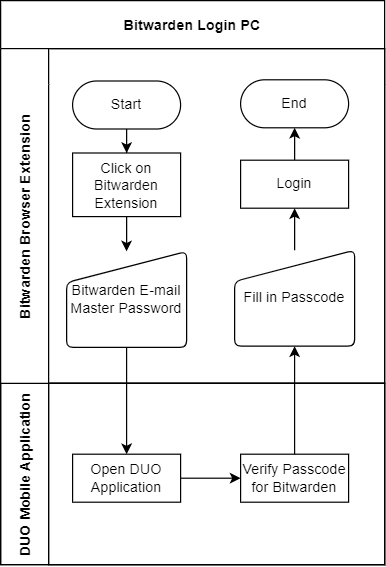
Below you can find a flowchart to show how I usually log in to any website or application when using the Bitwarden browser extension on my PC.
The difference between using the Bitwarden application on my phone is that I am not using a finger scan here. Instead of fingerprint biometrics authentication, I have to log in with the master password for every new browser session. This is something you can change in the Bitwarden application settings.
6. Lost Phone Recovery
For each of the previously shown authentication methods DUO is required to access the Bitwarden application that stores all my logins and most of the services I use are also configured for MFA through DUO. This means when I lose my phone or lose access to DUO I lose access to all websites and applications.
The only thing to notice is that Bitwarden only requires DUO pascodes for login in case you are logged out from the browser extension or application. A master password or fingerprint is sufficient to get access to Bitwarden in case it is only locked.
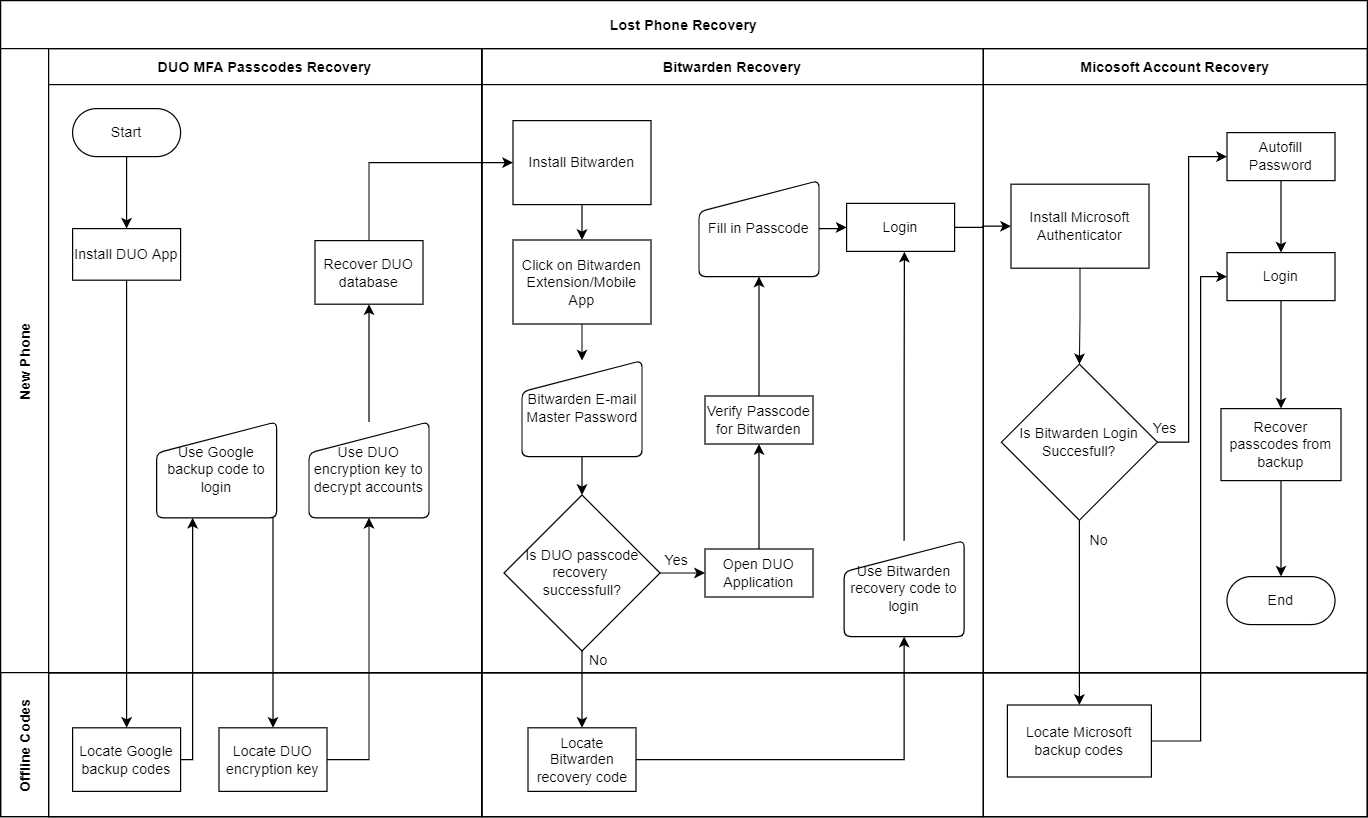
Below you can find a flowchart on how to recover access to DUO passcodes, Bitwarden and Microsoft Authenticator. I configured all three services in a way that each can separately be recovered with offline recovery codes.
7. Outro
There are many applications and many ways for implementing multi-factor authentication. Everyone can implement this in their way but I would recommend always having a backup method so you do not lock yourself out when you lose one of the ways of authenticating yourself.
You can verify at https://2fa.directory/ if the services you are using is compatible with a way of multi-factor authentication.

